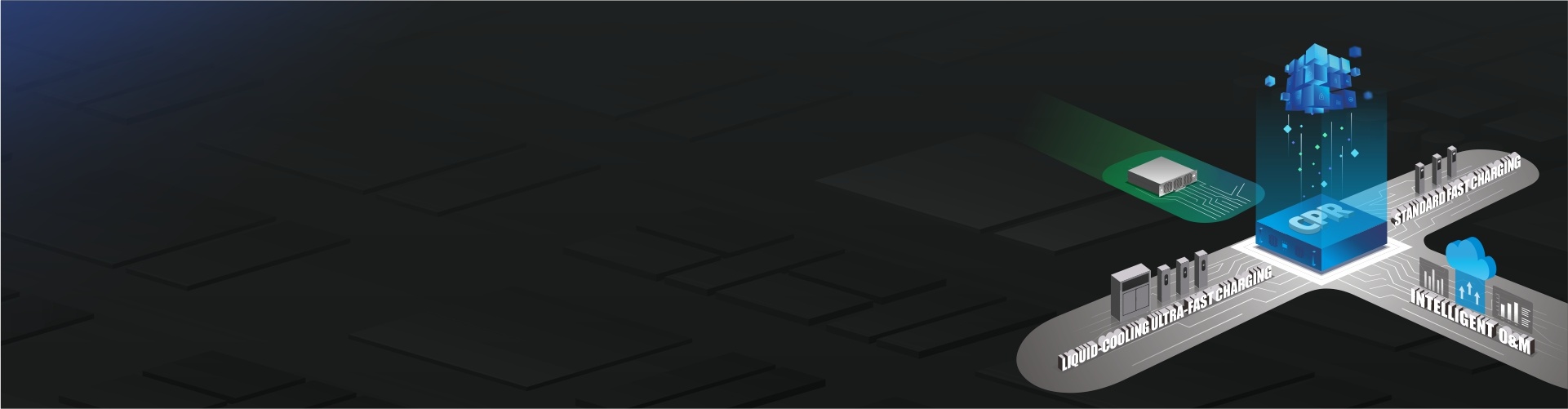
Charging Hub

Core value
Leveraging intelligent scheduling core products, XY Power can collaborate with customers to develop charging hub system products with greater commercial value.
Full-matrix intelligent scheduling for higher system efficiency.
Hardware and software development and maintenance are more convenient.
Modular design, with system cabinet design saving over 10% of space.
Recommended Products
XY Power Smart Charging Power Router
12-in and 6-out Charging Power Router
• The full matrix design offers more flexible scheduling and higher power utilization.
Supports parallel output, with a maximum single-circuit current of up to 3000A.
Flexible matching of 3 to 6 terminals according to scenario requirements.
What cooling method does the charging module use (air-cooled/liquid-cooled)? Can it operate stably in harsh environments such as high temperature and high humidity?
30/40kw charging module features forced air cooling, and the 60kw one features independent air-duct cooling. XY Power charging module is widely known as its reliability and efficiency, it’s market-proven to operate stably in harsh environments. Comparing with these two modules, the independent air-duct cooling module is rated IP65 and it has better adaptability to high temperature and high humidity.
What is the expected lifespan of the charging module? Does it require regular maintenance? If so, what is the frequency and approximate cost of maintenance?
The lifespan of a charging module is influenced by the longevity of several key components, primarily including fans, film capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, and others. XY Power intelligent operation and maintenance functionality enables the prediction and balancing of the lifespan of these critical components. This ensures higher reliability, extended lifespan, lower maintenance costs, and more precise operation and maintenance management throughout the entire lifecycle of the charging infrastructure.
Does the charging module support smart features such as remote monitoring, fault diagnosis, and OTA updates? Is it compatible with mainstream communication protocols like CAN?
Absolutely yes. Starting from the X2 generation, the charging modules from XY Power are equipped with an intelligent operation and maintenance system. These modules can upload more data through protocols, providing data and functional support for the intelligent operation and maintenance of charging stations or platforms. This enhances the overall reliability, extends the lifespan, reduces maintenance costs, and enables more precise operation and maintenance management throughout the entire lifecycle of the charging facilities.
The intelligent operation and maintenance system by XY Power can achieve lifespan prediction, fault warning, grid monitoring, environmental sensing, and system auxiliary functions.
How does this module distribute power intelligently?
The CPR module is a power distribution module used in split-type one-to-many DC charging pile systems. It dynamically and real-time adjusts the charging power of each terminal according to the minimum dispatch granularity of the charging pile system, ensuring optimal vehicle charging demand satisfaction and maximum equipment utilization.
What is the difference between full-matrix distribution and Partial-matrix distribution?
| Dimension | Full-matrix | Partial-matrix |
| Connection Topology | Fully interconnected input and output | Partially interconnected input and output |
| Dynamic Allocation Capability | Supports any input → any output | Only supports predefined input → output combinations |
| Redundancy | Extremely high (multiple backup paths) | Limited (relies on predefined paths) |
| Hardware Cost | High (requires a large number of switching components) | Low (simplified switches and wiring) |
| Control Complexity | High (requires real-time dynamic routing algorithms) | Low (based on rules or priority allocation) |
| Applicable Scenarios | High-fluctuation loads, multi-tenant shared scenarios | Stable loads, fixed charging terminal allocation scenarios |
Tech Trends & Recommendations
Full Matrix: Suitable for scenarios that demand extremely high flexibility and reliability (such as supercharging stations), but requires a trade-off between initial investment and long-term operational costs.
Partial Matrix: Ideal for large-scale deployments (such as battery swap stations), enabling "on-demand expansion" through modular design to reduce costs.
Hybrid Solution: Some manufacturers adopt a "layered matrix" approach (full matrix at the core layer + partial matrix at the edge layer), balancing flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
If there are specific charging pile architecture or parameter requirements, further details can be provided for a targeted analysis and optimization plan!
What is the difference between an AC charging station and a DC charging station?
An AC charging station converts AC power to DC power through the vehicle's onboard charger (OBC) to charge the battery, with lower power (usually 7kW-22kW), suitable for home or long-term parking scenarios. A DC charging station directly converts grid AC power to DC power and inputs it into the battery, with higher power, suitable for public and high-speed transportation networks.
What are the common issues and solutions for charging station installation?
1). Power configuration: Check the type of meter for the input AC pile. A single-phase meter is suitable for a 7kW pile, while a three-phase meter is suitable for 11kW/22kW.
2). Site requirements: An independent circuit and grounding protection are needed, avoiding sharing lines with high-power equipment, and adapting a reasonable circuit breaker in the upper-level circuit. For example, a 7kW pile requires a 40A single-phase Type B MCCB. Ensure there are no flammable materials around.
What may have effects on compatibility issues with charging station?
1). Connector compatibility design: Supports IEC charging interface (IEC 62196), compatible with mainstream vehicle models.
2). Vehicle-pile interoperability design: Supports the IEC 61851 standard AC communication protocol to ensure connection with the charging protocols of most vehicles on the market.
3). Comprehensive OCPP access capability ensures the ability to upgrade the entire pile and remotely resolve faults through OTA during use.
What is the role of PCS in an energy storage system?
PCS is the core power conversion component of an energy storage system. It accepts dispatch from the energy management system of the energy storage, enabling the bidirectional flow of electricity between the grid and the storage batteries. During peak electricity usage or when the grid requires support, the PCS converts the electrical energy from the storage batteries into AC power. During off-peak electricity usage or in response to grid demands, the PCS converts AC power into DC power to charge the batteries.